الدورات
title
MySQL vs PostgreSQL – Full Comparison With Examples
Below is the ultimate enterprise-grade comparison between MySQL and PostgreSQL, covering architecture, performance, indexing, JSON, search capabilities, extensions, ACID behavior, transactions, concurrency, geospatial features, replication, stored procedures, tree structures, and full SQL examples.
This version contains no icons and is suitable for publishing as an article, documentation, or technical proposal.
1. SQL Compliance
PostgreSQL
- Almost fully SQL standard compliant
- Supports advanced SQL features including:
- Window functions
- Materialized views
- Recursive CTE
- Full OUTER JOIN
- Custom operators
- Table inheritance
- Full-text search
- CROSS APPLY / LATERAL
Example – LATERAL join:
SELECT *
FROM users u
LEFT JOIN LATERAL (
SELECT *
FROM orders o
WHERE o.user_id = u.id
ORDER BY created_at DESC
LIMIT 1
) last_order ON TRUE;
MySQL
- Lower SQL compliance
- No native full outer join
- Fewer advanced SQL features
- Window functions only became usable in MySQL 8
2. Performance
PostgreSQL performs best for:
- Analytics
- Complex queries
- Heavy joins
- OLAP workloads
- JSON + relational hybrid applications
MySQL performs best for:
- Simple CRUD
- Read-heavy traffic
- High-speed small to medium applications
- Lightweight workloads
3. Index Types
PostgreSQL (Very Rich):
Supports:
- B-tree
- GiST
- GiN
- BRIN
- Hash
- Expression indexes
- Partial indexes
Example – Partial index:
CREATE INDEX idx_users_active ON users (email) WHERE active = true;
MySQL
Supports:
- B-tree
- Hash (Memory engine only)
Advanced index types like GiST and GiN are not available.
4. JSON Handling
PostgreSQL
- Industry-leading JSON support
- Full indexing
- JSONPath
- Custom operators
- Advanced querying
Example:
SELECT data->'address'->>'city'
FROM users
WHERE data @> '{"role": "admin"}';
MySQL
- Has JSON data type
- Limited operators
- No full JSON indexing
5. Full Text Search
PostgreSQL
- Built-in text search engine
- Ranking, weighting, stemming
- GiN index support
Example:
SELECT *
FROM articles
WHERE to_tsvector(content) @@ to_tsquery('database & engine');
MySQL
- Basic full-text search
- Limited ranking
- No stemming
- Few supported languages
Example:
SELECT *
FROM articles
WHERE MATCH(content)
AGAINST ('database engine' IN NATURAL LANGUAGE MODE);
6. Extensions & Customization
PostgreSQL
Extremely extensible. Supports modules such as:
- ltree (hierarchical data)
- postgis (geospatial)
- pgvector (AI embeddings)
- pg_cron
- uuid-ossp
- hstore
MySQL
- Limited extension ecosystem
- Must wait for vendor updates
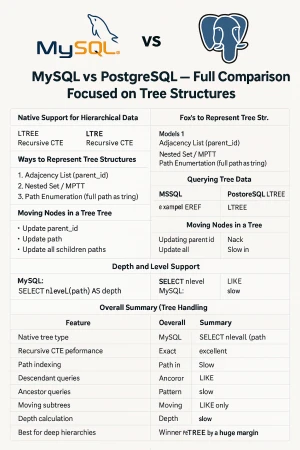
7. Tree Structures (Hierarchical Data)
Adjacency List Example (Supported by both)
SELECT * FROM categories WHERE parent_id = 5;
Recursive CTE Example (PostgreSQL & MySQL 8+)
WITH RECURSIVE c AS (
SELECT * FROM categories WHERE id = 12
UNION ALL
SELECT child.*
FROM categories child
JOIN c ON child.parent_id = c.id
)
SELECT * FROM c;
PostgreSQL executes this significantly faster.
PostgreSQL LTREE Example (PostgreSQL only)
Descendants:
SELECT * FROM categories WHERE path <@ 'lms.programming';
Ancestors:
SELECT * FROM categories WHERE path @> 'lms.programming.php.laravel';
MySQL
- No LTREE
- Must rely on
VARCHAR+LIKE, which becomes slow at scale
8. Concurrency (MVCC)
PostgreSQL
- True MVCC implementation
- Readers do not block writers
- Excellent for high-concurrency systems
MySQL
- MVCC depends on InnoDB
- More locking than PostgreSQL
9. Transactions & ACID
PostgreSQL
Fully ACID with:
- Serializable isolation
- Savepoints
- Nested transactions
Example:
BEGIN; INSERT INTO orders VALUES (...); SAVEPOINT s1; UPDATE accounts SET balance = balance - 100; ROLLBACK TO s1; COMMIT;
MySQL
- ACID only under InnoDB
- No nested transactions
10. Stored Procedures
PostgreSQL
Supports multiple languages:
- PL/pgSQL
- Python
- Perl
- JavaScript
- C
Example:
CREATE FUNCTION add_user(name text)
RETURNS void AS $$
BEGIN
INSERT INTO users(name) VALUES(name);
END;
$$ LANGUAGE plpgsql;
MySQL
- Only SQL-based stored procedures
- Much more limited
11. Replication
PostgreSQL
- Logical & physical replication
- CDC (Change Data Capture)
- Streaming replication
- Bidirectional replication
MySQL
- Strong replication support
- Master–slave replication
- Group replication
12. Security
PostgreSQL
- Role inheritance
- Row-level security (RLS)
- Rich permission model
Example:
ALTER TABLE users ENABLE ROW LEVEL SECURITY;
MySQL
- No row-level security
- Basic privilege system
13. GIS (Geospatial)
PostgreSQL (PostGIS)
- Industry standard
- Most advanced geospatial features available for SQL databases
Example:
SELECT ST_Distance(a.location, b.location) FROM areas a, areas b;
MySQL
- Basic GIS
- Not suitable for complex geospatial applications
14. AI & Vector Search
PostgreSQL (pgvector)
- Used by major AI platforms
- Supports vector indexing and ANN search
Example:
SELECT * FROM items ORDER BY embedding <-> '[0.1, 0.2, 0.3]' LIMIT 5;
MySQL
- No vector support
- Not suitable for AI workloads
Full Summary Table
FeatureMySQLPostgreSQLSQL Standard ComplianceLowHighPerformanceStrong for simple workloadsStrong for complex workloadsIndex TypesBasicAdvancedJSONGoodExcellentFull Text SearchBasicEnterprise-gradeExtensionsLimitedExtensiveTree StructuresWeakExcellent (LTREE + CTE)MVCCPartialFullGISBasicAdvanced (PostGIS)AI Vector SearchNot availableAvailable (pgvector)ReplicationGoodAdvancedSecurityBasicStrong with RLSStored ProceduresLimitedMulti-language






