الدورات
title
NodeStealer Malware Targets Facebook Ad Accounts and Harvests Credit Card Data

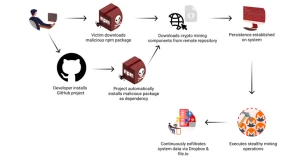
Cybersecurity researchers are sounding alarms about the enhanced version of the NodeStealer malware, a Python-based threat targeting Facebook Ads Manager accounts and stealing sensitive data, including stored credit card information.

Key Threat Highlights
- Facebook Ads Manager Exploitation:
- NodeStealer collects budget details and business information from Facebook Ads Manager, potentially using compromised accounts for malvertising campaigns.
- Advanced Techniques in Use:
- Leverages Windows Restart Manager to unlock browser database files.
- Employs junk code for obfuscation.
- Uses dynamic Python script generation via batch scripts for execution.
- Data Exfiltration via Telegram:
- Telegram remains a significant tool for threat actors to exfiltrate stolen information.
- Malvertising for Malware Propagation:
- Fake ads mimicking trusted brands (e.g., Bitwarden) have been used to distribute malicious extensions, infecting users and compromising business accounts.

Origins and Development
Originally identified by Meta in May 2023 as a JavaScript-based malware, NodeStealer has since evolved into a sophisticated Python-based stealer. Analysis suggests the malware is linked to Vietnamese threat actors known for hijacking Facebook business accounts to finance further malicious activities.
Key Capabilities of NodeStealer
- Facebook Business Account Takeovers:
- NodeStealer utilizes the Facebook Graph API to generate access tokens by logging into victims' accounts using stolen cookies.
- Avoidance of Law Enforcement:
- The malware includes mechanisms to avoid infecting systems located in Vietnam, indicating deliberate measures to evade local scrutiny.
- Credit Card Data Theft:
- By unlocking SQLite browser database files, the malware extracts stored credit card details and sensitive account information.
Emerging Campaigns and Malicious Tactics
- Fake Ads and Impersonation:
- Recent campaigns starting November 2024 used Facebook-sponsored ads to impersonate trusted software like Bitwarden. These ads distributed rogue Chrome extensions to harvest data and compromise accounts.
- ClickFix Phishing Technique:
- A rising social engineering tactic, ClickFix involves tricking users into executing encoded PowerShell scripts through fake CAPTCHA pages. This method bypasses security controls and exploits user behavior to self-infect devices.
Broader Implications and Threat Landscape
- Dual Exploitation Risks:
- Financial losses and operational disruptions for businesses and individuals due to compromised advertising and payment systems.
- Phishing and RAT Deployment:
- Techniques like fake Docusign requests and pornographic link campaigns deliver malware such as I2Parcae RAT, PythonRatLoader, and Venom RAT, targeting both financial and governmental entities.
- Persistent Threats via Social Engineering:
- Tactics leveraging fake CAPTCHAs and Docusign lures show how attackers exploit user trust and platform vulnerabilities to bypass traditional defenses.
Mitigation Strategies
- Implement Runtime Behavioral Analysis:
- Detect anomalous actions in applications and block threats before data exfiltration occurs.
- Educate Users on Phishing Risks:
- Raise awareness about tactics like ClickFix and ensure users understand the importance of verifying the legitimacy of unexpected error prompts or CAPTCHA checks.
- Strengthen Ad Account Security:
- Use multi-factor authentication (MFA) on Facebook and other business platforms.
- Regularly review ad campaign budgets and access permissions.
- Leverage Advanced Threat Detection Tools:
- Utilize security solutions capable of identifying obfuscated scripts, dynamic threats, and network anomalies.